PowerPath Migrator Enabler is a host-base migration tools from EMC that allows you to migrate data between storage systems with little or no interruption to data access. This tool can be use in conjunction with other underlying technology such as EMC Invista, Open Replicator. PPME use the PowerPath filter dirvers to provide non-disruptive or minimally disruptive migrations. Only specific host plateforms are supported by PPME. Please check EMC support matrix for supported host systems. One of the PPME features that supports pseduo-to-pseduo, native-to-native and native-to-pseudo device migration.
Consider the following when designing and configuring PPME:
Ø Remote devices do not have to be the same RAID type or meta-configuration.
Ø Target devices must be the same size or large than the source control device.
Ø Target directors act as initiators in the SAN.
Ø Contrary to the recommendations for Open Replicator, the source device remains online during the “hot pull.”
Ø The two storage systems involved in the migration must be connected directly or through a switch, and they must be able to communicate.
Ø Every port on the target array that allows access to the target device must also have access to the source device through at least one port on the source array. This can be counter to some established zoning policies.
Ø Since PPME with Open Replicator uses FA resources, determine whether this utility will be used in a production environment. In addition, consider FA bandwidth assessments so that appropriate throttling parameters (that is, pace or ceiling).
Ø The powermig throttle parameter sets the pace of an individual migration by using the pace parameter of Open Replicator:
Ø Faster (lower throttle) makes the migration faster, but may impact application I/O performance.
Ø Slower (higher throttle) makes the migration slower.
Ø The default is five (midpoint).
Ø When setting a ceiling to limit for Open Replicator throughput for a director/port:
Ø The ceiling value is set as a percentage of a director/port’s total capacity.
Ø The ceiling can be set for a given director, port, director and port, or all director and ports in the Symmetrix array.
Ø To set ceiling values, you must use symrcopy set ceiling directly (powermig does not provide a way to do this)
Ø Once the hot pull has completed, remove or re-use the source device.
Ø Do not forget to “clean up” the zoning once you have completed migration activities.
Hope this will be useful in migration planning or selecting migration tools. I will try to explain in deatil in coming post such as PPME with Open Replicator, Solution Enabler etc..
What is “Tier 0” in Storage Environments?
Tier "0" is not new in storage market but for implementation purposes it has been difficult to accommodate because it requires best performance and lowest latency. Enterprise Flash disks (Solid State Disks) capable to meet this requirement. It is possible to get more performance for company most critical applications. The performance can be gained through using Flash drives supported in VMAX and DMX-4 systems. Read More →
Showing posts with label PowerPath Pseudo Device. Show all posts
Showing posts with label PowerPath Pseudo Device. Show all posts
Lets first disuss what is Powerpath software. If you are familiar with EMC product and then definitelly will be using EMC Powerpath software.
Those who are new to storage world, it will interesting to know about this product as there are only few software in this category like DMP,PVLINK, LVM etc from other vendor. This sofware is one of the most robust compare to other, thats reason EMC generationg more revenue out of this Product.... .
EMC PowerPath software is Host/Server based failover software, what is that mean failover. failover can be anything like server,HBA,Fabric etc. If you have fully licenced package in your enviornment then you will have all capability. Most important not least this software got good feature like dynamic IO Loading and Automatic Failure detection which is missing in other product. Basically in short we can define that EMC PowerPath provides you to have HA configuration. EMC Powerpath slogan is like "set it and forget".
EMC PowerPath features a driver residing on the host above HBA Device Layer. This transparent componenet allows PowerPath to create Virtual(power) devices that provide failure resistant and load balanced paths to storage systems. An application needs only to reference a virt ual device while Powerpath manages path allocation to storage system.
With PowerPath, the route between server and storage system can assume a complex path. One powerpath device include as many as 32 physical I/O paths ( 16 for Clariion), with each path designated to the operating system by different name.
In most cases, the application must be reconfigured to use pseudo devices, otherwise PowerPath load balancing and path failover functionality will not be available.
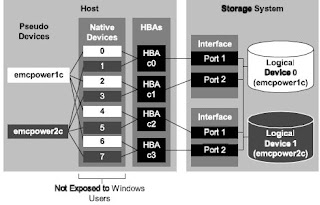
The following describe whether application need to be reconfigure to use pseudo devices.
1) Windows Plateform :- No. ( Application not require to reconfigured to use Pseudo Devices )
2) AIX :- NO- For LVM, Yes, if applicaiton do not use LVM
3) HP-UX - NO
4) Solaris :- Yes, Incluing filesystem mounting tables and volume managers.
5) Linux :- Same as Solaris
if you attach new LUN to Host, powerpath automatically detect that LUN if you have exposed correctly and create device name like emcpower1c, emcpower2c etc, even when you type command on CLI like
#powermt display dev=all;
you will be able to device entry like emcpowerN.....
Hope this will help you to understand why powerpath uses pseudo devices?
About Me

- Diwakar
- Sr. Solutions Architect; Expertise: - Cloud Design & Architect - Data Center Consolidation - DC/Storage Virtualization - Technology Refresh - Data Migration - SAN Refresh - Data Center Architecture More info:- diwakar@emcstorageinfo.com
Blog Disclaimer: “The opinions expressed here are my personal opinions. Content published here is not read or approved in advance by EMC and does not necessarily reflect the views and opinions of EMC.”


